| |
| |
Dietmar GLINDEMANN,
Publications as author and coauthor
Publications 58 (SciFinder Scholar Data Base)
Publications 55 (ISI Web of Knowledge Cited Reference Search)
Citations 2278 (ISI Web of
Knowledge Cited Reference Search) (16 Oct. 2022) |
| |
| |
|
Publications on Environmental
Analysis, Chemistry and Odor Research (phosphine, organophosphorus,
organometal, organosulfur, water + waste treatment) |
Reprint requests: E-mail:
dglinde@aol.com (or
click links below to download)
Dietmar GLINDEMANN,
www.glindemann.net
www.phosphine.net |
| |
| |

Odor of Money? Money does not smell - until humans touch it !
(click to enlarge)
Artwork: D. Glindemann / Angew. Chem.
|
|
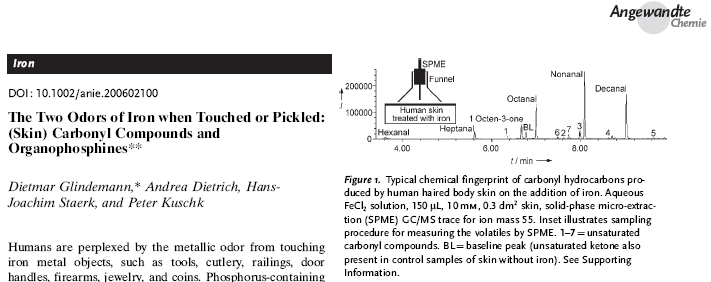
D. Glindemann, A.
Dietrich, H.-J. Staerk, P. Kuschk.
The Two Odors of Iron when
Touched or Pickled: (Skin) Carbonyl Compounds and Organophosphines.
Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2006), 118(42), 7006–7009. DOI:
10.1002/anie.200602100
In Deutsch:
D. Glindemann, A.
Dietrich, H.-J. Staerk, P. Kuschk.
Die zwei Gerüche des Eisens bei Berühung und unter Säureeinwirkung – (Haut-)Carbonylverbindungen
und Organophosphine. Angewandte Chemie (2006), 118(42), 7163–7166 (in Deutsch). DOI
10.1002/ange.200602100
Download Abstract and PDF of article from the Journal:
http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/113383440/ABSTRACT
Download "Supporting Information" for this article from the Journal:
http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2002/2006/z602100_s.pdf
(Request PDF-Reprint of this article from dglinde@aol.com)
(Request PDF of 15 pages of "Supporting Information" for this
article from dglinde@aol.com)
Externe Links zu dieser Publikation (Presse-Mitteilungen,
Zeitungsartikel...)
External links to this publication (press releases, news paper articles, dictionary...)
|
| |
Research on waste
water plant odor by industrial DMSO waste
Dietmar Glindemann discovered that Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
industrial waste in sewage produced an
odor problem in a wastewater plant in Philadelphia, USA. His research saved the
municipality of Philadelphia 20 million US-Dollars. |
here the most important of my DMSO publications
Glindemann, D., Novak, J., Witherspoon, J.
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Waste Residues and Municipal Waste Water Odor by
Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS): the North-East WPCP Plant of Philadelphia. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2006), 40(1), 202-207.
 Click to enlarge Abstract: This
study shows for the first time that overlooked mg/L concentrations of industrial
dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste residues in sewage can cause “rotten cabbage”
odor problems by dimethyl sulphide (DMS) in conventional municipal wastewater
treatment. Click to enlarge Abstract: This
study shows for the first time that overlooked mg/L concentrations of industrial
dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste residues in sewage can cause “rotten cabbage”
odor problems by dimethyl sulphide (DMS) in conventional municipal wastewater
treatment.
In laboratory studies, incubation of activated sludge with 1 to 10
mg/L DMSO in bottles produced dimethylsulfide (DMS) at concentrations that
exceeded the odor threshold by approximately four orders of magnitude in the
headspace gas. Aeration at a rate of six m3 air / m3
sludge resulted in emission of the DMS into the exhaust air in a manner
analogous to an activated sludge aeration tank.
A field study at the NEWPCP
sewage treatment plant in Philadelphia found DMSO levels intermittently peaking
as high as 2400 mg/L in sewage near an industrial discharger. After three hours,
the DMSO concentration in the influent to the aeration tank rose from a baseline
level of less than 0.01 mg/L to a level of 5.6 mg/L and the DMS concentration
in the mixed liquor rose from less than 0.01 to 0.2 mg/L. Finding this link
between the intermittent occurrence of DMSO residues in influent of the
treatment plant and the odorant DMS in the aeration tank was the key to
understanding and eliminating the intermittent “canned corn” or “rotten cabbage”
odor emissions from the aeration tank that had randomly plagued this plant and
its city neighborhood for two decades. Sewage authorities should consider having
wastewater samples analyzed for DMSO and DMS to check for this possible odor
problem and that DMSO emission thresholds be established to limit odor
generation at sewage treatment plants.
External
Links to this paper (Press
release of the American Chemical Society):
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2005-12/acs-dra122005.php
http://www.impactlab.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=6885
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2005/12/051221091407.htm
http://www.ens-newswire.com/ens/dec2005/2005-12-20-09.asp#anchor7
|
Other environmental DMSO publications of Dietmar Glindemann
Glindemann, D.
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) waste residues and municipal waste water
odor. WEFTEC 2005, 78th annual technical exhibition and conference, October 29-
November 2, 2005, Washington DC, USA. |
|
D. Glindemann, J.T. Novak and J. Witherspoon. Aeration tank odour by
dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) waste in sewage. Water Science & Technology Vol
55 No 5 pp 319–326 (doi:10.2166/wst.2007.194) |
|
|
|
Research on Environmental Chemistry and Odor
analysis of waste water and biosolids |
WERF
Report: Treatment Processes (00-HHE-5T (b)) Author(s): GM Adams, J Witherspoon
Publication Date: July 2004 · ISBN: 1843396874
(Impacts of in-plant operational
parameters on biosolids odor quality: preliminary results of WERF Phase 2 study.) |
|
Subramanian, R., Novak, J. T., Murthy, S. Glindemann, D., North, J.
Investigating the role of process conditions in wastewater sludge odor
generation. WEFTEC 2005, 78th annual technical exhibition and conference,
October 29- November 2, 2005, Washington DC, USA. |
|
Dietmar
GLINDEMANN at National Biosolids Odors Research Meeting @ Bucknell University, June 13,
2002 �Odor Research at Virginia Tech, CEE |
|
Murthy, S.; Forbes,
B.; Burrowes, P.; Esqueda, T.; Glindemann, D.; Novak,
J.; Higgins, M.; Mendenhall, T.; Toffey, W..
Impact of high
shear solids processing on production of volatile sulfur compounds from
anaerobically digested biosolids. WEFTEC.02, Conference Proceedings, Annual
Technical Exhibition & Conference, 75th, Chicago, IL, United States, Sept.
28-Oct. 2, 2002
(2002), 4494-4505. CODEN: 69EWYB CAN 140:258120 AN 2004:75703 CAPLUS |
|
Murthy, S..; Peot,
C.; North, J.; Novak, J.; Glindemann, D.; Higgins, M. Characterization and
control of reduced sulfur odors from lime-stabilized and digested biosolids.
Annual Residuals and Biosolids Management Conference: Privatization, Innovation
and Optimization: How to Do More for Less, 16th, Austin, TX, United States, Mar.
3-6, 2002 (2002), 775-794.
CODEN: 69EVNV CAN 140:239825 AN 2004:31753 CAPLUS |
|
Murthy S., Kim, H.,
McConnell, L., Peot, C., Bailey, W., Novak, J., and Glindemann, D. (2002).
“Mechanisms for odour generation during lime stabilization.” IWA Biennial
Conference, Melbourne, Australia. |
|
Novak, J.T.,
Glindemann, D., Murthy, S.N., Gerwin, S. and Peot, C. (2002) Mechanisms For
Generation and Control of Trimethyl Amine
and Dimethyl Disulfide From Lime Stabilized Biosolids.
WEF Odors and Toxic
Air Emissions 2002 Conference Proceedings, April 29-30, 2002,
Albuquerque, NM:. |
|
Forbes, R.H.,
Adams, G., Witherspoon, J., Hentz, L., Murthy, S., Glindemann, D., Higgins, M.;
Card, T., Hargreaves, J.R., and Erdal, Z..
Impacts of in-plant
operational parameters on biosolids odor quality: preliminary results of WERF
Phase 2 study. WEF/AWWA/CWEA Joint Residuals and Biosolids Management
Conference and Exhibition: Partnering for a Safe, Sustainable Environment,
Baltimore, MD, United States, Feb. 19-22, 2003 (2003), 565-585.
CODEN: 69EZAU CAN
140:326141 AN 2004:79842 CAPLUS |
|
Forbes, B.; Adams, G.; Hargreaves, R.; Witherspoon, J.; McEwen, D.; Erdal, Z.;
Hentz, L.; Murthy, S.; Card, T.; Glindemann, D.; Higgins, M.. Impacts of the
in-plant operational parameters on biosolids odor quality. Final results of WERF
odor project Phase 2 field and laboratory study. WEF/A&WMA Odors and Air
Emissions 2004, Specialty Conference, Bellevue, WA, United States, Apr. 18-21,
2004 (2004), 454-467. |
|
Higgins, M.J., S.N. Murthy, J.T.
Novak, D.P. Yarosz and D. Glindemann, Toffey, W.E. and Abu-Orf, M.M.
2002.
Effect of Chemical addition on Production of Volatile Sulfur Compounds and Odor
from Anaerobically Digested Biosolids.
Proceedings of Water Env. Fed.
75th Annual Conf., Chicago. |
|
M. Abu-Orf; J. Brewster, J. Oleszkiewicz, R.S. Reimers, P. Lagasse, B. Amy; D.
Glindemann.
Production of Class
A Biosolids With Anoxic Low Dose Alkaline Treatment and Odor Management Issues.
IWA Norway
Conference, Norway, 2003. |
|
Abu-Orf, M. M.; Brewster,
J.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Reimers, R. S.; Lagasse, P.; Amy, B.; Glindemann, D..
Production of class A biosolids with anoxic low dose alkaline treatment and odor
management.
Water Science and Technology (2004), 49(10, Wastewater Sludge as a Resource),
131-138 |
|
Abu-Orf, Mohammad
M.; Brewster, J.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Reimers, R. S.; Lagasse, P.; Amy, B.;
Glindemann, D.. Production of Class A biosolids with anoxic low
dose alkaline treatment and odor management. Wastewater Sludge
as a Resource, Proceedings of the International Water Association (IWA)
Specialist Conference, BIOSOLIDS 2003: Wastewater Sludge as a Resource,
Trondheim, Norway, June 23-25, 2003 (2003),
177-184 |
|
Higgins, M.J., Yarosz, D. P.,
Chen, Y. C., Murthy, S. N., Maas, N., Cooney, J., Glindemann, D., and
Novak, J. T. (2006) Cycling of volatile organic sulfur compounds in
anaerobically digested biosolids and its implications for odors. Water Env.
Res., 78, 243-252. |
|
Adams, G.M.,
Witherspoon, J., Card, T., Erdal, Z., Forbes, B., Geselbracht, J., Glindemann,
D., Hargreaves, R., Hentz, L., Higgins, M., McEwen, D., and Murthy, S.,
Indentifying and Controlling the Municipal Wastewater Odor Environment Phase 2:
Impacts of In-Plant Operational Parameters on Biosolids Odor Quality.
2003, Water Environment
Research Foundation: Alexandria, VA. |
|
Porter, R., Witherspoon, J., Daigger, G., Fahnestock, L., Novak, J.T.,
Glindemann, D., Burlingame, G., Choudhary, S.A., Lendzinski, R., Suffet, M.,
and Rosenfeld, P.
ASSESSMENT OF ODOR FORMATION MECHANISMS IN AN ACTIVATED SLUDGE BASIN AT THE
NORTHEAST WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT. WEFTEC 2004, 77th annual technical
exhibition and conference, October 2-6, 2004, New Orleans, USA. |
|
Novak, John T.; Adams, Gregory; Chen, Yen-Chih; Erdal, Zeynep; Forbes, Robert
H., Jr.;
GLINDEMANN, Dietmar; Hargreaves, J. Ronald; Hentz, Lawrence; Higgins,
Matthew J.; Murthy, Sudhir N.; Witherspoon, Jay; Card, Thomas. Odor
generation patterns from anaerobically digested biosolids. WEF/A&WMA
Odors and Air Emissions 2004, Specialty Conference, Bellevue, WA, United States,
Apr. 18-21, 2004 (2004), 521-530. |
|
Higgins, M. J.; Adams, G.; Card, T.; Chen, Y.C.; Erdal, Z.; Forbes, R. H.;
Glindemann, D.; Hargreaves, J. R.; Hentz, L.; McEwen, D.; Murthy, S. N.;
Novak, J. T.; Witherspoon, J.. Relationship between biochemical constituents
and production of odor causing compounds from anaerobically digested biosolids.
USA. WEF/A&WMA Odors and Air Emissions 2004, Specialty
Conference, Bellevue, WA, United States, Apr. 18-21, 2004 (2004),
438-453. |
|
Subramanian, Rahul; Novak, John T.; Murthy, Sudhir; GLINDEMANN, Dietmar;
North, Jason. Investigating the role of process conditions in wastewater sludge
odor generation. Proceedings - Water Quality Technology Conference and
Exhibition (2005), 6582-6604. |
|
Glindemann, D., Murthy, S., Higgins, M. J., Chen, Y. C., Novak, J. T.
Biosolids incubation method for odorous gas measurement from dewatered sludge
cakes. Journal of Residuals Science and Technology. 2006, 3(3), 153-160 |
| |
| |
|
Dietmar
GLINDEMANN 's Publications on Phosphine and Organometallics
in the Environment
The full text of most of the following publications is
available by clicking on the titles:
(to receive a free reprint by EMail (as PDF file) email dglinde@aol.com |
|
Phosphine-publications at University of Leipzig and at Glindemann
Environmental Services |
|
Gassmann, G., Glindemann, D.: Phosphan in der Biosphäre.
Angew.Chemie 105, 749-751; Phosphane in the Biosphere. Angew.Chem.Intern.Edit. 32
(1993) 761-763 Link |
|
Glindemann, D., Bergmann, A. (1995):
Spontaneous emission of phosphane from animal slurry treatment
processing.
Zentralblatt für Hygiene und Umweltmedizin 198 , 49-56 |
|
Glindemann,D., Bergmann,A.,
Stottmeister,U., Gassmann, G. (1996) Phosphine in the lower terrestrial troposphere.
Naturwissenschaften 83 (1996) 131-133 |
| Gassmann, G., Glindemann, D., van Beusekom, J. Offshore
Atmospheric Phosphine. Naturwissenschaften 83 (1996) 129-131 |
|
Glindemann, D., Stottmeister, U.,
Bergmann, A.: Free phosphine from the anaerobic biosphere. Environ.Sci.&Pollut.Res. 3
(1996) 17-19 |
| Glindemann,D., Morgenstern,P.,
Wennrich,R., Stottmeister,U., Bergmann,A.: Toxic Oxide Deposits from the Combustion of
Landfill Gas and Biogas. Environ.Sci.&Pollut.Res. 3 (1996) 75-77 |
|
Eismann, F., Glindemann, D., Bergmann,
A., Kuschk P.: Soils as a source and sink of phosphine. Chemosphere 35 (1997)
523-533 |
|
Eismann, F., Glindemann, D.,
Bergmann, A., Kuschk, P.: Effect of free phosphine on anaerobic digestion. Water Research 31
(1997) 2771-2774 |
|
Eismann, F., Glindemann, D.,
Bergmann, A., Kuschk, P.: Balancing phosphine in manure fermentation. J. Environ. Sci.
Health, Part B 32 (1997) 955-968 |
Glindemann, D., Eismann, F., Bergmann, A., Kuschk, P.,
Stottmeister, U. Phosphine by Bio-Corrosion of Phosphide-Rich Iron. Environ. Sci. &
Pollut. Res. 5 (1998) 71-74
(anaerobic bacterial corrosion of
iron with a high phosphorus content, can explain published reports on "Free Phosphine" in biogases and on "Matrix Bound Phosphine" in sludges, sediments
etc.) |
|
Glindemann,
D., De Graaf, R.M., Schwartz, A.W.: Chemical reduction of phosphate on the primitive
earth. Origins of life and evolution of the biosphere 29 (1999) 555-561 |
| Cao
HF, Liu J, Zhuang YH, Glindemann D: Emission sources of
atmospheric phosphine and simulation of phosphine formation.
SCIENCE IN CHINA SERIES B-CHEMISTRY 43: (2) 162-168 APR 2000 |
| Liu JA, Yahui CHZ,
Kuschk P, Eismann F, Glindemann D:
Phosphine in the urban air of Beijing and its possible sources.
WATER AIR AND SOIL POLLUTION 116: (3-4) 597-604 DEC 1999 |
| Han
SH, Zhuang YH, Liu JA, Glindemann D: Phosphorus cycling through phosphine in paddy fields.
SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT 258 (3): 195-203 AUG 30 2000 |
|
Han SH, Wang ZJ, Zhuang YH,
YU ZM, Glindemann D: Phosphine in various matrixes. Journal of Environmental
Sciences 15, 339-341 (2003) |
|
Niu XJ, ... Glindemann D, et al. - Determination of Phosphine in
Shallow Eutrophic Water by Gas Chromatography. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,
31, 378 pp (2003) |
|
/Niu, XJ, Zhang JF, Shi
XL, Wang XR, Gao GA, Ji JA, Glindemann D. Studies on Microcystis aeruginosa
affected by phosphine and its oxidation dynamically released from eutrophic
lakes. Journal of Lake Sciences (China), 15, 263-268 (2003). |
|
Zhu, Renbin; GLINDEMANN, Dietmar; Kong, Deming; Sun,
Liguang; Geng, Jinju; Wang, Xiaorong. Phosphine in the marine atmosphere along a
hemispheric course from China to Antarctica. Atmospheric Environment (2007),
41(7), 1567-1573. |
|
Zhu, Renbin; Kong, Deming; Sun, Liguang; Geng, Jinju; Wang, Xiaorong;
Glindemann, Dietmar. Tropospheric Phosphine and Its Sources in Coastal
Antarctica. Environmental Science & Technology (2006), 40(24), 7656-7661.
|
| |
|
Phosphine-publications at Virginia Tech, Department of Civil and
Environmental Engineering, with
Prof. Marc Edwards |
|
Glindemann, D.,
Edwards, M., Kuschk, P. Phosphine gas in the upper troposphere.
Atmospheric Environment 37 (2003) 2429–2433 |
|
Glindemann, D., Edwards, M., Schrems, O. Phosphine and methylphosphine
production by simulated lightning – a study for the volatile phosphorus cycle
and cloud formation in the earth atmosphere. Atmospheric Environment 38 (2004)
6867-6874. |
|
Glindemann, D.; Edwards, M.; Liu, J. A.; Kuschk, P. Phosphine in soils, sludges,
biogases and atmospheric implications—a review. Ecological Engineering 24 (2005)
457–463 |
|
Glindemann, D., Edwards, M., Morgenstern, P. Phosphine from Rocks - Mechanically
Driven Phosphate Reduction?
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8295-8299 |
|
Niu XJ, Geng JJ, Wang XR,
Wang CH, Gu XH, Edwards M, Glindemann D. Temporal and spatial distributions of
phosphine in Taihu Lake, China. Science of the Total Environment 323 (2004)
169–178. |
|
Ding, LL; Wang, XR; Zhu YX; Edwards, M; Glindemann, D. Ren, HQ. Effect of pH
on phosphine production and the fate of phosphorus during anaerobic process with
granular sludge. Chemosphere 59 (2005) 49–54 |
|
Ding LL, Liang HW, Zhu YX, Mo WH, Wang Q, Ren HQ, Wang XR, Edwards M,
Glindemann D. Sources of matrix-bound phosphine in advanced wastewater treatment
system CHINESE SCIENCE BULLETIN 50 (12): 1274-1276 JUN 2005 |
|
Geng JJ, Jin XC, Wang Q, Niu XJ, Wang XR, Edwards M, Glindemann D. Matrix
bound phosphine formation and depletion in eutrophic lake sediment fermentation
- simulation of different environmental factors. Anaerobe 11 (2005) 273–279 |
|
GENG JJ, NIU XJ, JIN XC, WANG XR, HUANG YA, EDWARDS M, GLINDEMANN D.
Simultaneous monitoring of phosphine and of phosphorus species in Taihu Lake
sediments and phosphine emission from lake sediments. Biogeochemistry (2005) 76,
283–298 |
|
Morton, Siyuan C.;
GLINDEMANN, Dietmar; Edwards, Marc A. Phosphates,
Phosphites, and Phosphides in Environmental Samples. Environmental Science and
Technology (2003), 37(6), 1169-1174 |
|
Morton, S. C., Glindemann, D., Wang, X. R., Niu, X. J. and Edwards,
M. A (2004) Analysis of reduced phosphorus in samples of environmental
interest. Environ. Sci. Technol.2005, 39,4369-4376 |
|
Glindemann, D., Edwards, M., Morgenstern, P. Phosphine from Rocks - Mechanically
Driven Phosphate Reduction?
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8295-8299 |
|
|
|
|
Other papers of Dietmar
GLINDEMANN
(Organometal Environmental chemistry, Physico-chemistry, ...) |
Glindemann, D., Ilgen, G., Herrmann, R., Gollan, G.
Advanced GC/ICP-MS design for high-boiling analyte speciation and large volume
solvent injection.
JAAS, 17 (2002) 1386 - 1389 (October)
(now a widely accepted interface to connect GC with ICP
spectrometers, large volume injection, prevention of graphite deposition, less
than 150 oC transferline temperature, almost unlimited interface length and
flexibility)
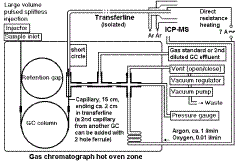 Click to enlarge Click to enlarge |
| Feldmann, J., Krupp, E.M., Glindemann, D.,
Hirner, A.V., Cullen, W.R.: Methylated Bismuth in the Environment: Applied Organometallic
Chemistry 13 (1999) 739-748. |
Cullen WR, Andrewes P, Glindemann D, Lehr C,
Polishchuk E
Group 15 derivatives in the environment: The cause of sudden infant death syndrome?
ABSTRACTS OF PAPERS OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY 218: 343-INOR , Part 1 AUG 22 1999 |
Glindemann,D.,
Maskow,T., Browarzik,D. Kehlen,H., Kutscha,J.:
Role of Azeotropy in Characterization of Complex Hydrocarbon Mixtures by Fractionated
Distillation.
Fluid Phase Equilibria 135 (1997) 149-167
Thermodynamics of True Boiling Point
Distillation Rectification (TBP, ASTM D1160, ISO 6616, Crude Oil...)
Before this publication, a myth existed that a distillation process with
sufficiently high separation power can
Dietmar Glindemann was the first who explored that compounds
of multi-component-mixtures (crude oil, petroleum, fuels etc.) that contain
different chemical classes like alkanes, aromates, alkoholes.) can not be
separated according to their true boiling points by True Boiling Point
Distillation (analytical TBP distillation). Even at an infinite number of
theoretical plates of distillation (rectification), aceotropic effects cause
that individual compounds to not distill over as pure compounds but as
mixtures.
Interestingly, these aceotropic effects of TBP were BEFORE its
experimental detection already theoretically
predicted by Dietmar Glindemann using a thermodynamic model of distillation with
an infinite number of theoretical plates of distillation. This theory was
successfully tested by experiments of the research team by using sophisticated
distillation apparatus with a high number of theoretical plates of distillation.
|
Raetzsch, M. T.; Glindemann, D. Application of the increment method UNIFAC to
concentrated polymer solutions. Acta Polymerica (1979), 30(1), 57-60.
Dietmar Glindemann measured by "inverse gaschromatography (GC)" thermodynamic
activity coefficients of industrial solvents (injected) in industrial polymers
(as GC stationary phases). |
| |
|
Glindemann D., Glindemann U. Greaseless Taper Jointed Glassware and Containers
hermetic tight
with
new PTFE Sealing Ring. Fusion 2001, 48(2) 29-33
(FUSION is the journal of the American Scientific Glassblowers Society ASGS)

|
|
|
Links to Phosphine in the
environment
http://www.degeschamerica.com, use of phosphine for food protection
The Organometallic HyperTextBook, Phosphine Complexes
Undertaining book on Phosphorus:
The 13th Element, by John Emsley
reviewed by Daniel Rabinovich, Department of Chemistry, The University of
North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 28223, Wiley: New York, 2000.
327 pp. ISBN 0-471-39455-6. $24.95. |
|
|




 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge